All about pips in forex: a comprehensive guide
Discover what pips are in forex trading and how to calculate their value. Learn about their impact on risk management and trading strategies.
What is a pip?
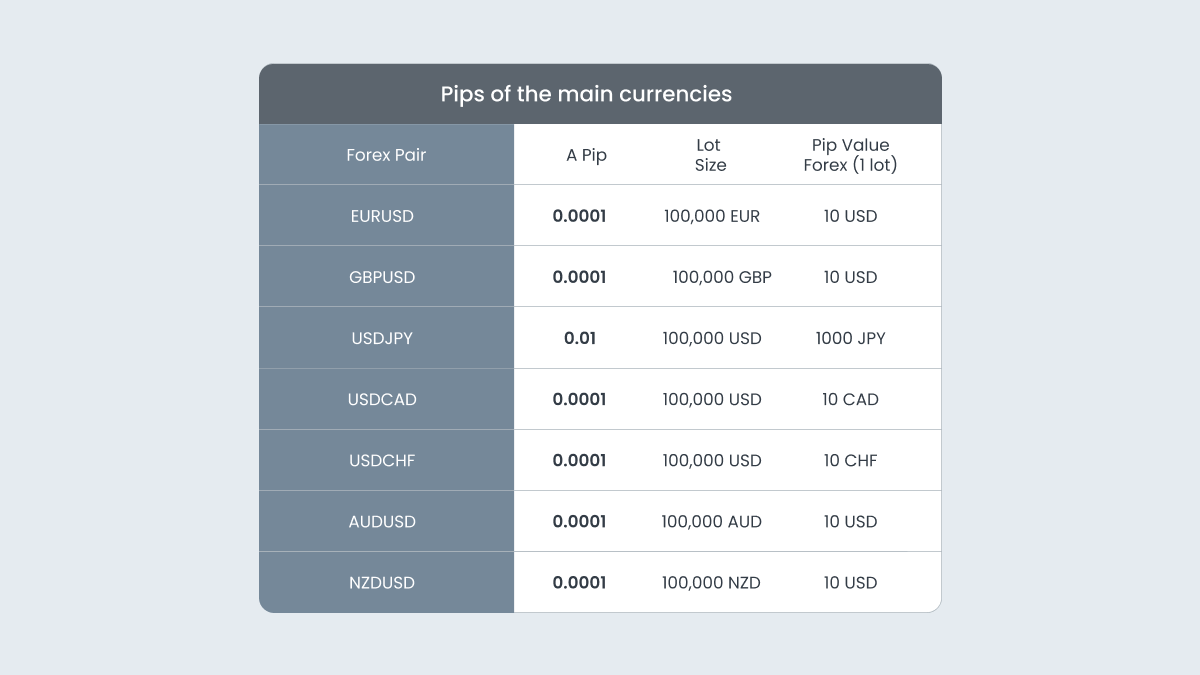
A pip is a forex market convention, and it used to be the smallest unit of price movement that an exchange rate could make. A pip equals one-hundredth of 1% (1/100 × 0.01), and appears in the fourth decimal place (0.0001). Although there are now more precise methods for pricing (with more decimal places), the pip remains a standard value for brokers and trading platforms.
In most currency pairs, the quotation is made to four decimal places, and a pip is found in the fourth decimal (i.e., 1/10,000). For example, the smallest movement that the USDCAD currency pair can make is $0.0001, or one pip. The term "pip" is an acronym of "percentage in point", or "price interest point". It is important to note that a pip should not be confused with a basis point (bps), as the latter is used in interest rate markets and represents 0.01% or one-hundredth of 1%.
What is a pip in forex?
A pip is a fundamental concept in the forex market. It is a standard unit used in the forex market to measure the change of an asset’s price. People engaged in forex trading buy and sell a currency whose value is expressed in relation to another currency. The quotes for these currency pairs are shown in the form of bid and ask spreads, which are accurate up to four decimal places.
This unit of measurement is small enough to capture fluctuations in exchange rates, without resorting to fractions or more complex numbers. The value of a pip varies depending on the size of the traded lot. For example, if a standard lot of 100 000 units of the base currency is traded, each pip is worth about 10 units of the counter currency in the quote.
This standardization makes it easier to understand and compare price changes in currency pairs, and is a great help in developing safe trading plans.